In the world of construction, manufacturing, and heavy industry, the success of a massive project can often depend on the smallest components. A simple fastener, if it fails, can lead to catastrophic consequences. This is why understanding the materials and specifications of components like the carbon steel U-bolt is not just a technical detail—it’s a critical business imperative. As a factory owner who has been producing these essential parts for years, I, Allen, have spoken with hundreds of procurement officers like you. I understand your need for quality, reliability, and value. This guide is written from my first-hand experience to demystify the carbon steel U-bolt, explain why it’s a superior choice for high strength applications, and help you make purchasing decisions with confidence.
What Exactly is a Carbon Steel U-Bolt?
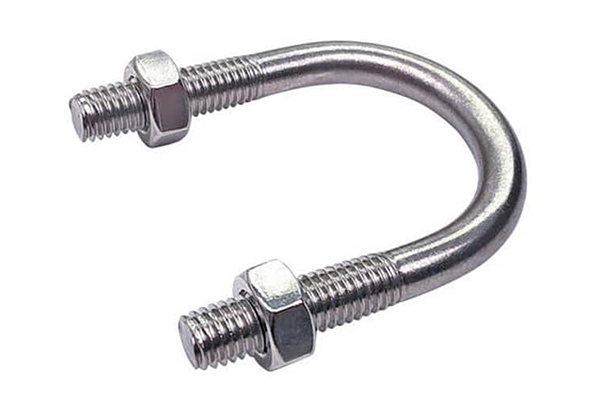
At its core, a U-bolt is a simple yet incredibly effective fastener shaped like the letter ‘U’, with screw thread on both ends. Its primary function is to support or secure pipes, tubes, cables, or other cylindrical objects. The U-shaped design allows it to wrap around the object, and it’s then secured in place with nuts and a plate on the other side, creating a firm clamp. This design is fundamental in everything from automotive suspensions to industrial pipeline support.
When we talk about a carbon steel U-bolt, we are referring specifically to the material it’s made from. Carbon steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, renowned for its incredible strength and durability. Unlike softer metals, it can withstand immense tension and pressure, making it the ideal material for heavy-duty fastening. These u-bolts are the workhorses of the industrial world, providing the structural integrity needed to hold critical systems together safely and securely.
Why is Carbon Steel the Go-To Material for High-Strength U-Bolts?
When a project demands raw strength, carbon steel is almost always the answer. The reason lies in its metallurgical properties. The carbon content in the steel alloy acts as a hardening agent, significantly increasing the material’s tensile strength—its ability to resist being pulled apart. This makes carbon steel u-bolts far stronger than those made from many other materials, including most grades of stainless steel.
In applications involving heavy machinery, structural support, or high-vibration environments, you need a fastener that won’t stretch, bend, or break under load. That’s the promise of carbon steel. We also have the ability to heat-treat carbon steel u-bolts to further enhance their mechanical properties, achieving specific hardness and tensile ratings required by engineering standards like ASME. This combination of inherent strength and the ability to be precisely treated makes carbon steel u the preferred choice for engineers and contractors who cannot compromise on safety and performance.
Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel U-Bolts: Which is Right for Your Application?
This is a question I get all the time from procurement professionals. The choice between carbon steel and stainless steel for your u-bolts depends entirely on the application’s environment and requirements. It’s a classic trade-off between strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Stainless steel u-bolts are known for their excellent resistance to rust and corrosion. This is due to the addition of chromium, which forms a passive, protective layer on the surface. They are ideal for marine environments, food processing plants, or any application with high moisture or exposure to corrosive chemicals. However, stainless steel generally has a lower tensile strength than heat-treated carbon steel and is significantly more expensive.
On the other hand, carbon steel u-bolts offer superior strength at a much more cost-effective price point. Their primary vulnerability is corrosion. However, this is easily overcome with protective coatings, which we’ll discuss next. For most industrial and construction applications where maximum load-bearing capacity is the priority and the environment is controlled or can be protected, carbon steel is the superior and more economical choice.
| Feature | Carbon Steel U-Bolt | Stainless Steel U-Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Very High (Especially when heat-treated) | Good to High (Varies by grade) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low (Requires protective coating) | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower / More Cost-Effective | Higher |
| Best For | Heavy-duty structural, industrial, and automotive applications. | Marine, chemical, and food-grade applications where rust is a major concern. |
How Does Galvanization Protect a Carbon Steel U-Bolt?
Since carbon steel is susceptible to rust, we need a way to protect it. The most common and effective method for a fastener like a u-bolt is galvanization. This process involves applying a protective zinc coating to the steel. The zinc acts as a sacrificial barrier; if the coating is scratched, the zinc will corrode before the steel does, dramatically extending the service life of the u-bolt.
There are a few ways to galvanize a part, but for high-quality u-bolts used in harsh environments, the best method is hot-dip galvanization. In this process, the finished u-bolt is submerged in a bath of molten zinc, creating a thick, durable, and metallurgically bonded coating. This hot-dip galvanized layer provides far more robust corrosion resistance than a simple zinc plated finish, which is much thinner. A hot-dip coating ensures that your carbon steel u-bolt can withstand outdoor exposure and tough industrial settings for decades.
What Key Specifications Should You Check When Ordering U-Bolts?
As a procurement officer, getting the specification right is crucial. An incorrect size or thread can bring a project to a halt. When ordering u-bolts, you need to be precise. Here are the essential details a supplier like me needs to manufacture your order correctly:
- Material Type: Be specific (e.g., Grade 5 Carbon Steel, Type 316 Stainless Steel). This determines the strength and environmental resistance.
- Diameter (A): The diameter of the rod material itself.
- Inside Width (B): The distance between the legs of the u-bolt. This is critical for fitting around a pipe.
- Inside Length / Leg Length (C): The length of the legs from the inside of the top to the end of the threaded ends.
- Thread Specification (D): This includes the thread pitch (e.g., UNC for coarse, UNF for fine) and the length of the thread on each leg.
- Finish/Coating: Specify the required protective coating (e.g., Hot-Dip Galvanized, Zinc Plated, Plain Finish).
- Compliance Standards: If the u-bolts must meet certain standards (e.g., ASME, ASTM), this must be clearly stated.
Providing these clear specifications ensures you receive the exact fastener you need, avoiding costly delays and errors. Don’t hesitate to provide a technical drawing if you have one. Clear communication is key to a successful partnership. The nuts you choose are just as important, and you can see a variety of options on our Nut page.
Understanding the ‘High Strength’ in High-Strength U-Bolts
The term “high strength“ isn’t just a marketing buzzword; it refers to specific mechanical properties defined by industry standards. For carbon steel u-bolts, strength is typically measured by their grade, which corresponds to their tensile strength—the maximum stress they can withstand before breaking. For example, an SAE Grade 5 carbon steel u bolt has a minimum tensile strength of 120,000 pounds per square inch (PSI). A Grade 8 u-bolt, made from a higher-grade alloy steel, can exceed 150,000 PSI.
This high tensile strength is critical for applications where the fastener is under constant tension or subject to shock loads, such as in vehicle suspensions or securing heavy equipment. The choice of material—whether it’s a standard carbon steel u or a more complex alloy steel u-bolt—is determined by the load requirements of the engineering design. A reputable manufacturer will be able to provide documentation certifying the material grade and its corresponding strength ratings, giving you peace of mind that the u-bolts made for your project meet the required safety factors.
Where are These Carbon Steel Fastening Solutions Most Commonly Used?
Because of their strength and versatility, carbon steel u-bolts are widely used across various industries. Their primary function is to act as a robust clamp or anchor point. You will find them in virtually every heavy-duty sector.
- Construction and Infrastructure: U-bolts are used to secure building components, anchor support systems, and fasten rebar. They are also fundamental in securing pipework for water, gas, and drainage.
- Oil and Gas: In this sector, u-bolts are essential for creating reliable pipeline support systems, securing pipes to structural beams and preventing movement caused by vibration and thermal expansion.
- Automotive and Transportation: They are a key component in leaf spring suspensions for trucks and heavy vehicles, holding the axle securely to the spring assembly.
- Telecommunications: U-bolts are used to attach antennas, dishes, and cables to towers and masts.
- Manufacturing: They secure mechanical equipment, motors, and conveyor systems to their foundations.
The common thread across all these applications is the need for a reliable, high strength fastening method that is also cost-effective, making the carbon steel u-bolt an indispensable component. Many of these applications also require high-quality bolts, which you can explore on our Bolt page.
How Do You Choose the Right Size and Thread for Your U-Bolt?
Choosing the right size and thread is a practical decision based on the object you are securing. The inside width of the u-bolt should correspond to the outside diameter of the pipe or component it will be holding. It’s important to allow for a small amount of clearance for easy installation, but not so much that it creates a loose fit.
The thread specification is equally important. Coarse threads (UNC) are more common in industrial applications. They are more tolerant of nicks and dings and are faster to assemble and disassemble. Fine threads (UNF) have greater tensile strength due to a larger stress area and allow for finer adjustments, but they are more susceptible to being damaged or cross-threaded. For most heavy-duty fastening, a coarse thread is the standard and recommended choice for your u bolt. Always ensure that the nuts you use have a matching thread type and material grade to maintain the integrity of the entire assembly.
What are the Dangers of Using a Low-Quality Fastener?
As a procurement officer, you understand the pressure to manage costs. However, opting for a cheap, low-quality fastener is one of the riskiest decisions you can make. The potential consequences far outweigh any initial savings. A substandard u-bolt can lead to catastrophic failure, causing property damage, project delays, and, most importantly, serious safety hazards.
Low-quality u-bolts are often made from inferior steel with inconsistent alloy content, leading to a much lower load-bearing capacity than advertised. They may have improperly formed thread, which can strip easily under torque. Furthermore, a poor galvanize coating can flake off, leaving the carbon steel exposed to premature corrosion and weakening the entire structure over time. Sourcing your fastener products from a reputable manufacturer with verifiable quality control is the only way to ensure the safety and longevity of your project. This is true for all structural components, including support systems like our Mine welding wire support mesh.
Finding a Reliable Partner for Your U-Bolts and Fastening Solutions
Your choice of supplier is just as critical as your choice of u-bolt material. A reliable partner is more than just a vendor; they are an extension of your team. When evaluating suppliers, especially overseas, clear communication and trust are paramount. A good supplier will be transparent about their materials, their manufacturing processes, and their quality certifications (like ISO 9001).
At my factory, we understand the pain points of international procurement. We prioritize clear, efficient communication to overcome language and time zone barriers. We provide complete documentation for our materials and welcome third-party inspections. We know that shipment delays can derail your projects, so we manage our logistics proactively. Our goal is to provide you not just with a high-quality carbon steel u bolt, but with a seamless and reliable supply chain for all your fastening solutions. We are here to build a long-term relationship based on performance and trust.
Key Takeaways
Selecting the right carbon steel U-bolt is a crucial decision for ensuring the safety and durability of any major project. Here are the most important things to remember:
- Strength First: Carbon steel offers superior tensile strength compared to stainless steel, making it the ideal choice for heavy-duty and high-load applications.
- Protection is Key: For corrosion resistance, always specify a hot-dip galvanized coating, which provides a thick, durable layer of zinc protection for your carbon steel u-bolts.
- Specifications Matter: Be precise with your order details—material grade, dimensions, thread type, and finish—to ensure you receive the correct fastener for the job.
- Don’t Compromise on Quality: Using a low-quality fastener is a major safety risk. Always partner with a reputable manufacturer who can provide verifiable quality certifications.
- The Right Material for the Job: While carbon steel is best for strength, stainless steel u-bolts are necessary for highly corrosive environments. Choose based on the specific application needs.
- Supplier Relationship: A good supplier is a partner who communicates clearly, provides transparent documentation, and understands the importance of on-time delivery.
Post time: Dec-31-2025