1. Structure and Working Principle of Pipe Seam Anchors
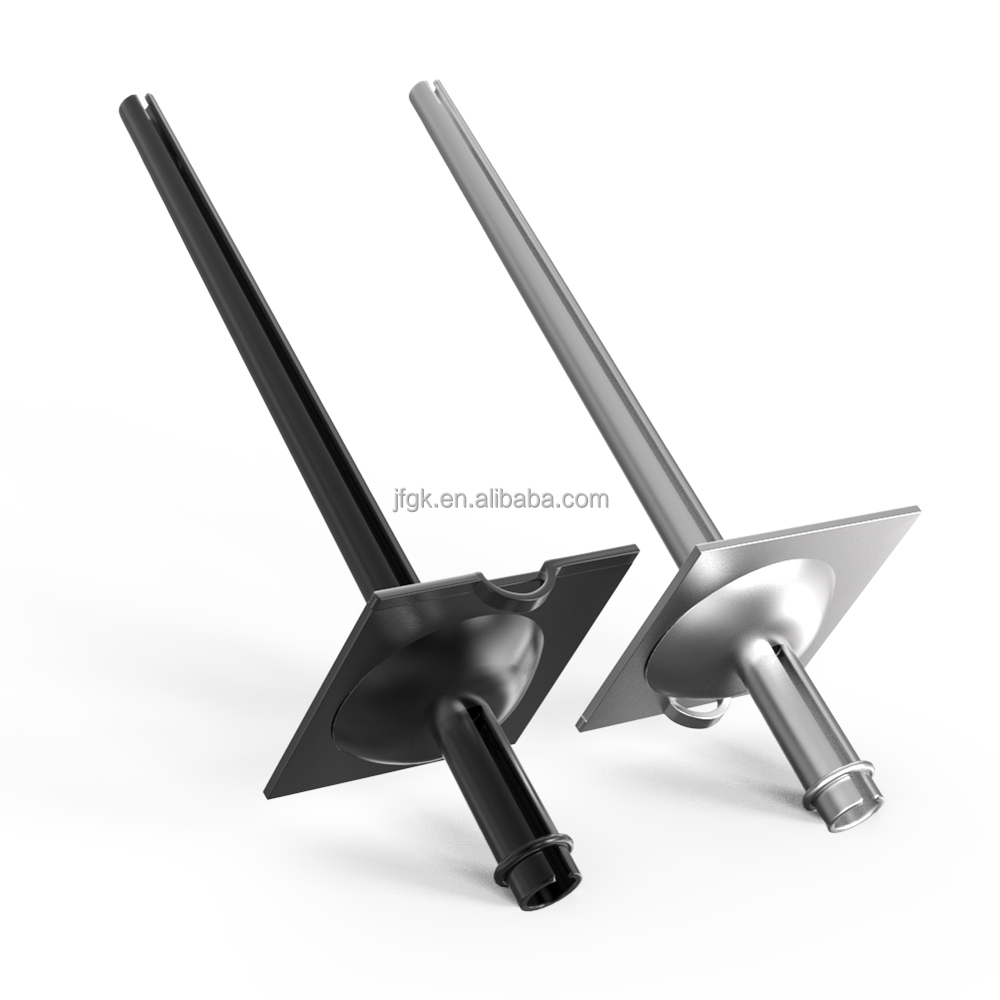
Pipe seam anchors are high-strength steel tubular devices designed for efficient mine roof and wall support. Their unique construction includes:
Longitudinal Seam: A continuous gap along the steel pipe enables elastic radial deformation.
Tapered End: Facilitates smooth insertion into drill holes.
End Plate Assembly: Applies pre-tensioning force via nut/washer systems to enhance stability.
Complete Support System Components:
Loading Plate: 150×150×6-10 mm square steel plate for load distribution.
Fastening Nut: Thread-matched to anchor ends for preload application.
Spherical Washer: Ensures uniform force transmission between plate and nut.
Anti-Loosening Device: Maintains tension in high-vibration environments.
Working Mechanism
Pipe seam anchors utilize a friction-based anchoring system:
Installation: Driven into a drill hole slightly smaller than its diameter.
Radial Expansion: Elastic contraction generates outward pressure against the hole wall.
Friction Lock: High surface friction stabilizes surrounding rock, preventing displacement.
2. Key Advantages Over Traditional Anchors
Pipe seam anchors outperform resin/mortar anchors in mining applications due to:
✅ Immediate Load-Bearing: No curing time required (vs. resin’s 30+ minute wait).
✅ Cost Efficiency: 40-60% lower material costs; reusable in temporary supports.
✅ Simplified Logistics: No chemicals or mixing equipment needed.
✅ Adaptability: Effective in fractured, soft, or wet strata where grouting fails.
Case Example: At Shandong’s 850m-deep coal mine, pipe seam anchors reduced support installation time by 70% compared to resin bolts, with zero roof falls during 12-month monitoring.
3. Installation Best Practices
Step-by-Step Guide
Drilling: Use rotary drills to create holes 2-4mm smaller than anchor diameter (e.g., 28mm hole for 30mm anchor).
Insertion: Drive anchor using hydraulic ram until plate contacts rock surface.
Tensioning: Tighten nut to 100-150 N·m torque (varies by rock class).
QC Check: Verify 5-10mm plate deflection under load for proper engagement.
Pro Tip: In highly fractured zones, combine with wire mesh for enhanced surface retention.
4. Industry Applications & Future Trends
Widely adopted in:
Coal mine roadways (80% of Chinese state-owned mines)
Tunnel reinforcement (notably in Australia’s Bowen Basin)
Emergency roof support in burst-prone strata
Emerging Innovations:
Smart Anchors: IoT-enabled versions with real-time load monitoring (pilot tested in Chilean copper mines).
Hybrid Systems: Pipe seam + micro-pile composites for ultra-deep (1,200m+) applications.
Conclusion
As mining depths increase and geological challenges grow, pipe seam anchors offer a reliable, economical, and rapidly deployable solution. Their friction-based design eliminates dependency on bonding agents, making them ideal for dynamic mining environments. For optimal results, engineers should:
🔹 Conduct geomechanical assessments to select anchor diameter/spacing
🔹 Implement regular torque audits to maintain preload integrity
🔹 Integrate with complementary systems (e.g., shotcrete) in high-stress zones
Need a customized support solution? [Contact our engineering team] for a free mine stability analysis.
Post time: Jun-23-2025