When you’re in the business of construction, mining, or geotechnical engineering, the tools you choose can make or break a project. The humble drill bit is at the forefront of this, and a seemingly small detail—the shape of its shank—has a massive impact on performance, safety, and efficiency. You’ve likely seen both round and hexagonal shanks, but what’s the real story behind them? This article dives deep into the world of the hex shank, explaining exactly what it is, how it differs from traditional round shanks, and why it might be the superior choice for your demanding jobs. As a manufacturer with over a decade of experience, I, Allen, will share insights directly from the factory floor to help you, the professional, make more informed decisions. We’ll explore everything from torque transfer to bit slippage, ensuring you understand how to get the most out of your drill.
What Exactly Is a Hex Shank on a Drill Bit?
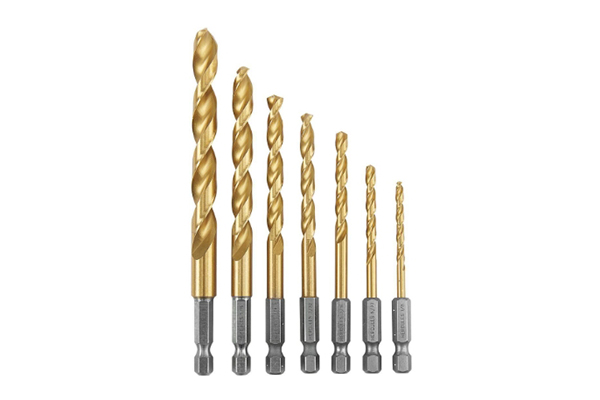
Let’s start with the basics. The “shank” is the end of the drill bit that you insert into the drill‘s chuck. It’s the part the drill grabs onto. While many traditional bits have a smooth, cylindrical, or round shank, a hex shank has a hexagonal shape—six distinct flat sides. This design isn’t just for looks; it’s a specific engineering choice meant to solve a common problem in drilling. Think of it like a nut and a wrench. A wrench can grip a hexagonal nut far more securely than it could a round one. The same principle applies here.
The most common size for a hex shank is 1/4-inch, which has become a standard for many impact drivers and quick-change systems. However, larger hex shank drill bits exist for heavy-duty applications, such as those using a powerful drill press or a robust hand drill. The core concept remains the same regardless of size: the flat surfaces provide multiple points of contact for the chuck‘s jaws to clamp down on, creating a mechanical lock that is far more secure than the friction-based grip on a round shank. This fundamental difference is the key to all the advantages a hex shank offers.
As a manufacturer, we see the direct impact of this design choice. The precision required to manufacture a perfectly symmetrical hex shank is significant. It must be perfectly balanced to prevent wobbling at high speed. The material, often high-speed steel, must be hardened to withstand the immense forces exerted by a modern drill without deforming. This attention to detail ensures that when you use a hex shank drill bit, it performs reliably every single time, providing a stable and efficient cutting experience.

How is a Hex Shank Drill Bit Different from a Round Shank?
The primary difference lies in how the drill chuck interacts with the shank. A round shank relies purely on the compressive force of the three jaws in a standard drill chuck. The jaws tighten and press into the smooth, round surface. While this works for many light-duty tasks, it has a significant weak point: under high torque, the round shank can slip inside the chuck. This slippage not only stops the drill bit from cutting effectively but also generates heat, which can damage the shank and the chuck‘s jaws.
A hex shank drill bit, on the other hand, creates a positive, mechanical interlock. The flat surfaces of the hexagonal shank sit flush against the jaws of a compatible chuck or driver. When the drill applies rotational force, the jaws push against these flats, preventing any possibility of the drill bit spinning independently of the chuck. This eliminates slippage almost entirely. This distinction becomes critically important when you’re drilling into tough materials like hard wood or metal, or when using a high-power electric drill.
To put it simply, here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | Round Shank Drill Bit | Hex Shank Drill Bit |
|---|---|---|
| Grip Mechanism | Relies on friction from the chuck jaws. | Mechanical lock between flat surfaces. |
| Slippage Risk | High, especially under heavy load or high torque. | Extremely low, almost non-existent. |
| Torque Transfer | Inefficient; some energy is lost to potential slip. | Highly efficient; nearly 100% of the drill‘s torque is transferred. |
| Compatibility | Fits in standard three-jaw drill chucks. | Fits in three-jaw chucks and 1/4” hex quick-change collets. |
| Bit Changes | Requires loosening and tightening the chuck with a key or by hand. | Allows for rapid, one-handed bit changes in compatible drivers. |
This fundamental design variance influences everything from the speed of your work to the lifespan of your tools. For professionals whose time is money, the efficiency gains from eliminating slip and enabling faster bit changes are a significant advantage.
What is the Main Advantage of Using a Hex Shank Drill?
The single greatest advantage of a hex shank drill system is superior torque transfer and the near-total elimination of slippage. When you are using a drill for a demanding task—like driving a large screw into dense wood or drilling a hole through a steel plate—you need all the power your drill can muster. With a round shank bit, as the resistance increases, the chuck might lose its grip. The drill motor will be spinning, but the drill bit itself will either slow down or stop completely, often with a screeching sound. This is a moment of failure.
A hex shank solves this problem elegantly. Because the chuck or collet locks onto the flat sides of the shank, it can’t slip. This ensures that every bit of rotational force (torque) generated by the drill‘s motor is delivered directly to the tip of the drill bit. The result? Faster, more consistent, and more powerful drilling. You can tackle tougher materials with more confidence and less frustration. This efficiency boost is not just a minor convenience; it directly translates to getting jobs done faster and with less strain on both the operator and the tool.
Beyond raw power, this secure grip makes the entire drilling process safer and more accurate. A slipping drill bit can mar the surface of your workpiece or, worse, cause the drill to jerk unexpectedly in your hands. A hex shank drill bit stays put, allowing for smoother entry into the material and better control throughout the drilling of the hole. This is particularly vital in woodworking or metalworking, where a clean, precisely placed hole is essential. The confidence that your drill bit will not slip allows you to focus on the task at hand, leading to better craftsmanship and a higher-quality finished product.
Can You Use a Hex Shank Drill Bit in a Regular Drill Chuck?
Yes, absolutely! This is one of the most practical features of hex shank drill bits. You can securely mount a hex shank bit into a standard three-jaw drill chuck, just like you would with a round shank bit. The three jaws of the regular chuck will close in and grip the flat surfaces of the hex shank. While you might not get the instant “click” of a quick-change system, the grip will still be significantly better than on a round shank bit.
When you tighten the drill chuck onto a hex shank, the jaws make solid contact with at least three of the six flat sides. This provides a much more secure hold than the tangential points of contact on a round shaft. So, even if you don’t own an impact driver or a drill with a dedicated hex collet, you can still reap the primary benefit of a hex shank: reduced slippage. This makes hex shank bits incredibly versatile. You can buy one set of quality bits and use them across multiple tools, from your trusty old electric drill with a keyed chuck to a modern, lightweight impact driver.
This compatibility is a huge plus for professionals like our typical customer, Mark, who manages procurement for his company. It simplifies inventory. Instead of needing separate sets of bits for different types of drills, his teams can use a single, high-quality set of hex shank drill bits for nearly all their applications. This is not only more cost-effective but also makes life easier for the crews on site. There’s no need to hunt for a specific type of bit; they can just grab the drill they need and know their hex bit will fit and perform well. This is a simple but powerful way to streamline operations.

Are There Specific Drills Designed for Hex Shank Bits?
Yes, and this is where the hex shank system truly shines. While they work great in a standard drill chuck, hex shanks are specifically designed for two types of modern power tools: impact drivers and drills with quick-change hex chucks. These tools are built to maximize the benefits of the hexagonal design.
Impact Drivers: These tools are designed to deliver high levels of rotational torque in short, powerful bursts. They are perfect for driving long screws or loosening stubborn bolts. Impact drivers exclusively use a 1/4-inch hex collet. To insert a bit, you simply push it into the collet until it clicks into place. There’s no manual tightening needed. This system is designed to handle the immense, sudden torque an impact driver produces—a force that would cause a round shank in a regular chuck to slip instantly.
Drills with Quick-Change Chucks: Many modern cordless drills and some drill presses are now equipped with a 1/4-inch hex quick-change chuck instead of the traditional three-jaw version. Like an impact driver, you just slide the hex shank in to lock it and pull back on the collet to release it. This allows for incredibly rapid bit changes, a feature that can save a significant amount of time on a job site where you’re frequently switching between drilling pilot holes and driving screws. For example, a carpenter framing a wall can switch from a spade bit for running wires to a Phillips bit for securing studs in a matter of seconds.
From our perspective as a factory, we often advise clients on pairing the right tool with the right accessory. For tasks involving high torque or frequent bit swaps, we strongly recommend using a drill or driver designed specifically to hold a hex shank. The synergy between the tool and the bit unlocks a level of performance and convenience that a traditional setup cannot match. Investing in a compatible tool is an investment in efficiency.
When Should You Choose Hex Shank Drill Bits Over Others?
Choosing the right drill bit shank often comes down to the specific application. While round shank bits are perfectly fine for general, low-torque tasks, there are several scenarios where a hex shank drill bit is the clear winner.
- High-Torque Applications: Any time you are drilling into dense or hard materials, a hex shank is the superior choice. This includes:
- Drilling into hard wood like oak or maple, especially with larger bits like an auger or forstner bit.
- Cutting holes in metal sheets or structural steel.
- Using self-feeding bits that pull themselves aggressively into the material.
- Driving long, large-diameter screws or lag bolts.
The anti-slip grip ensures maximum power is delivered to the cutting part of the bit.
- Using an Impact Driver: If you are using an impact driver, you must use a hex shank bit. These tools are not compatible with round shanks. Furthermore, it’s crucial to use bits that are “impact-rated.” An impact-rated hex shank bit is made from more ductile steel that can absorb the shock of the impacts without shattering. A standard hex bit might break under the stress.
- Jobs Requiring Frequent Bit Changes: For projects that involve constantly switching between different types of bits (e.g., a brad point bit for a clean pilot hole, then a countersink bit, then a driver bit), the speed of a quick-change system is invaluable. Professionals in cabinetry, furniture making, or deck building can save enormous amounts of time over the course of a day. This is where the combination of a quick-change drill and a set of hex shank bits truly boosts productivity.
In my experience talking to procurement officers like Mark, the decision often boils down to performance and reliability. When project deadlines are tight, you can’t afford to have a drill bit slip or waste time fumbling with a chuck key. For any serious professional, investing in a quality set of hex shank drill bits is a wise decision. For the most demanding jobs, such as installing our self-drilling hollow anchor systems, a powerful drill with a secure hex shank interface is not just a preference; it’s a necessity.
What Are the Common Types of Hex Shank Drill Bits Available?
The hex shank design is so versatile that it has been applied to nearly every type of drill bit imaginable. This means you can build a comprehensive drilling and driving kit using a single, convenient shank style. Here are some of the most common types you’ll find:
- Twist Drill Bits: These are your all-purpose bits for drilling holes in wood, metal, and plastic. Hex shank versions are often made from high-speed steel (HSS) and may feature a titanium or black oxide coating to reduce friction and increase longevity.
- Brad Point Bits: A favorite in woodworking, these bits have a sharp spur at the center tip that prevents the bit from “walking” or wandering when you start a hole. The result is a clean, exceptionally accurate hole.
- Spade Bits: Also known as paddle bits, these are used for quickly boring larger diameter holes in wood. Their flat design is perfect for rough-in work, like drilling holes through studs for electrical wiring or plumbing.
- Forstner Bits: For creating clean, flat-bottomed holes in wood, a Forstner bit is unmatched. They are essential for fine woodworking, cabinetry, and installing certain types of hardware. The hex shank provides the torque needed to power these large bits through hard wood.
- Auger Bits: These bits feature a deep, helical flute (the twist) and a screw tip that pulls the bit into the wood, making them ideal for drilling deep holes quickly and clearing chips efficiently.
- Driver Bits: This is perhaps the most common use for the 1/4” hex shank. Sets include Phillips, flathead, Torx, and square drive bits for driving any type of screw.
We manufacture a wide range of these tools, including some highly specialized multi-specification rock thread drilling drill bits that are built for the toughest geological conditions. The principle is the same: whether you’re drilling rock or wood, the interface between the drill and the bit must be flawless.
How Does a Hex Shank Prevent Slip and Improve Torque?
The physics behind the superiority of the hex shank is straightforward but powerful. It’s all about converting rotational force into useful work with minimal loss. A traditional three-jaw chuck holding a round shank relies entirely on friction. The jaws exert a high clamping force, and the static friction between the steel jaws and the steel shank is what keeps the bit from slipping. However, there’s a limit to this frictional force. When the drill encounters high resistance—for instance, when the cutting edge hits a knot in a piece of wood—the required torque can exceed this limit. The chuck is still spinning, but the bit isn’t. This is called “breaking static friction,” and once it happens, the bit slips.
Now, consider the hex shank drill bit. The jaws of the chuck (or the internal mechanism of a hex collet) are no longer just pressing against a curved surface. They are braced against large, flat planes. When the drill rotates, the jaws push directly on these flat surfaces. It’s like using a wrench on a bolt head. The force is perpendicular to the surface, creating a mechanical block. To make a hex shank slip, you would need to apply so much torque that you physically shear off the corners of the steel shank or destroy the jaws of the chuck—a scenario that requires catastrophic levels of force, far beyond what any handheld drill can produce.
This direct, mechanical engagement ensures that virtually 100% of the drill‘s motor torque is transferred to the bit. There is no energy wasted on friction or slippage. This efficiency has a cascading effect:
- Faster Drilling: More power at the tip means the cutting edges can do their job more effectively.
- Less Heat Buildup: Slippage is a major source of heat. By eliminating it, both the drill bit and the drill chuck stay cooler, extending their lifespan.
- Longer Battery Life: For cordless drills, every bit of wasted energy drains the battery. Efficient torque transfer means you can drill more holes on a single charge.
For professionals using tools like shank adapters to connect powerful rock drills, this principle of positive engagement is absolutely critical. In heavy-duty drilling, there is no room for slippage.
What Should I Look for When Buying High-Quality Hex Shank Drill Bits?
As a buyer like Mark knows, not all tools are created equal, especially those coming from a competitive global market. When a supplier claims to have a quality product, you need to know what to look for to verify that claim. Here are the key factors to consider when purchasing hex shank drill bits:
- Material: The type of steel used is paramount.
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): This is the standard for quality drill bits. It can withstand high temperatures without losing its hardness.
- Cobalt Alloys: For drilling into extremely hard materials like stainless steel, bits with a 5-8% cobalt blend are superior. They are more heat-resistant than standard HSS.
- Impact-Rated Steel (e.g., S2 Steel): For bits intended for impact drivers, look for a more flexible, shock-resistant steel like S2. This prevents them from shattering.
- Coatings: A coating is applied to enhance performance and longevity.
- Black Oxide: Offers basic corrosion resistance and reduces friction. A good, entry-level option.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): A very hard ceramic coating (usually gold-colored) that increases surface hardness and extends the life of the bit. The Bosch brand, for example, often uses high-quality coatings. We find that quality on par with these Bosch ones is what discerning customers expect.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN): Harder than TiN, offering even better wear resistance.
- Manufacturing Precision:
- Shank Geometry: A quality hex shank will be perfectly symmetrical with sharp, clean edges. A poorly made one might be slightly rounded, which can lead to a sloppy fit and eventual wear in the chuck.
- Flute Grinding: The spiral grooves (flutes) on a twist bit should be precisely ground to ensure efficient chip evacuation. Poorly formed flutes can cause the bit to bind in the hole.
- Tip Geometry: The cutting tip should be sharp and ground to the correct angle (a 135-degree split point is common for metal drilling as it prevents walking).
- Certifications: Always ask a potential supplier about their quality control and certifications. As a factory, we proudly adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which govern our quality management systems. This ensures consistency and traceability from raw materials to the finished product. A supplier who is hesitant to provide documentation or seems evasive about their quality process is a major red flag. For Mark, whose business reputation relies on supplying reliable tools, this is non-negotiable.
How to Care for Your Hex Shank Drill Bits to Prevent Wear?
Even the highest quality drill bit will become dull and ineffective if not cared for properly. Proper maintenance is key to maximizing the life of your investment and ensuring your bits are always ready for the job. Preventing premature wear saves money and frustration.
First, always use the right drill bit for the material. Using a wood bit on metal will destroy it almost instantly. Likewise, use the correct speed and pressure. Forcing a drill too hard or running it at too high a speed generates excess heat, which is the primary enemy of a sharp cutting edge. The steel can lose its temper, making it soft and quick to dull. A good rule of thumb is: the harder the material, the slower the drill speed.
Second, keep your bits clean and cool. When drilling metal, using a proper cutting fluid is essential. It lubricates the cutting action and, more importantly, dissipates heat. For wood, periodically pulling the bit out of a deep hole to clear the wood chips from the flutes can prevent binding and overheating. After use, wipe your bits clean of debris and store them in a dry place to prevent rust.
Finally, learn to recognize when a bit needs sharpening or replacement. A dull drill bit is inefficient and dangerous. It requires more force to cut, which increases the risk of the tool slipping or the workpiece splitting. Signs of a dull bit include squealing sounds, smoke coming from the hole, and having to apply excessive pressure. While some bits can be resharpened (especially larger HSS bits), smaller bits or those with complex coatings are often more economical to replace. By taking these simple steps, you can significantly extend the life of your hex shank drill bits and ensure they perform at their best every time you reach for your drill.
Key Takeaways to Remember
To wrap it all up, here are the most important points to remember about hex shank drill bits:
- Superior Grip: The six flat sides of a hex shank create a mechanical lock in the drill chuck, virtually eliminating the slippage common with round shanks.
- Efficient Torque Transfer: This secure grip ensures that nearly 100% of the drill‘s power is delivered to the bit’s tip, resulting in faster, more powerful drilling.
- Versatile Compatibility: Hex shank bits can be used in standard three-jaw drill chucks as well as in impact drivers and quick-change systems, making them incredibly versatile.
- Ideal for Demanding Jobs: They are the best choice for high-torque applications, such as drilling in hard wood or metal, and for jobs requiring frequent and fast bit changes.
- Quality Matters: When purchasing, pay close attention to the material (HSS, Cobalt), any performance-enhancing coatings (like Titanium), and the precision of the manufacturing. Always partner with suppliers who can prove their quality with certifications like ISO 9001.
Post time: Jul-10-2025